To lower their carbon footprints, many people are seeking solutions to heating systems that use alternative sources of energy. Electric heat pumps draw energy energy from the ground or air to cool or warm the interior of your home.
Eliminating or simply reducing fossil fuel based heating and energy can save money, and also helps clean the air inside your home. The absence of combustion in your home means that no exhaust gases circulate through the air that you live in each day. Fresh air in your home is among the major advantages when switching to a heat pump system.
ASHP Vs GSHP The Comparison
A word of caution: we shouldn’t make too broad a generalisation, as every project has particular strengths. These recommendations are based upon what we believe to be the most common trends. They should not be taken as gospel, since your specific situation is individual.
Please also note: the Renewable Heat Incentive closed to new applications on 31 March 2022.
In terms of the financials initially, we generally prefer an horizontal ground heat pump system because it is the most sought-after energy-efficient heating method. This is the most cost-effective option in the medium to long-term, but of course, it’s not appropriate for all properties and alternative solutions do have to be considered in the event that this option isn’t suitable for the requirements of the project.
We suggest vertical ground source heat pumps due to two reasons. In the first place, when you think of ground source in comparison to. air source as a whole, ground source is more efficient. Secondly, the Renewable Heat Incentive (RHI) price that applies to ground sources is greater than the amount you would expect from air source heat sources. This is especially true to larger buildings, since there are limitations on the amount of energy you can claim reimbursement for that is 20,000kW in air source, and 3000kW for ground source therefore, if you own an extra large house that requires more than 20,000kWh annually, it is sensible to examine ground source.
Another reason behind our preference lies when it comes to vertical as opposed to horizontal ground heat sources. We prefer horizontal as the installation costs are lower and simpler because of the equipment and experience required to dig trenches versus boreholes.
Ground Source Heat Pumps (GSHP)
These systems utilise the earth to act as a heat sink drilling below the surface temperatures. This can go approximately 8 inches deep within the United States.
Under the frost layer the earth is able to maintain a constant temperature of around 55 degree Fahrenheit. This is the basis for a stable geothermal cooling and heating system.
In geothermal energy system that uses a closed loop pipe, it can be placed either vertically or horizontally in the ground around the house. Then, water or other liquid is circulated inside the pipes, circulating through the stable temperatures of the earth, capturing the heat energy.
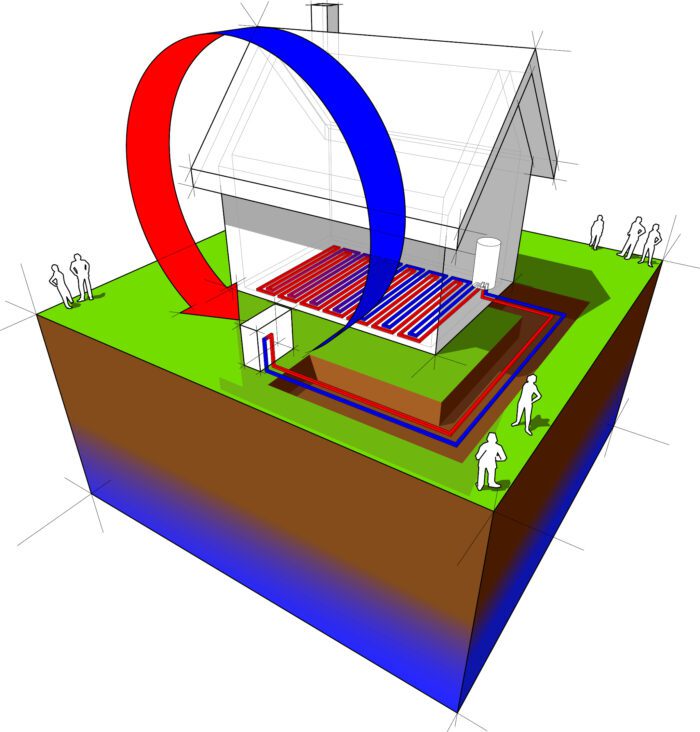
ground source heat pump diagram
The liquid transports the underground heat back to the heat pump in the home. It then releases the heat to the air in the house, heating it up, without burning fuel.
In summer the heat pump pulls heat from the air inside your house and lets it into the ground via the same pipes. Then , the cooler water of the surrounding earth is returned to your house and released as natural dehumidified air conditioning.
The earth around it is a great place to absorb heat in winter, and to get rid of heat during summer.
The fact that temperature doesn’t fluctuate too much during extremely hot or very cold weather creates an HVAC system that is able to function well even in extreme temperatures, which can result in homeowners substantial savings on their utility bills in addition to the high costs of winter fuels as well as AC in summer.
Air Source Heat Pumps (ASHP)
They are typically located outdoors, either on the rear or the side of a house. The heat is absorbed from the air and then boosted up to higher temperatures with the heat pump. While the pump needs electricity to operate but it requires lesser electrical energy as compared to the heat that it creates. A majority of ASHPs that are on the market are eligible for reimbursement by the Renewable Heat Incentive (RHI). These heat sources comprise 87% of the heat pumps in UK which is the highest sought-after choice among heat pumps. This is due to the fact that the air source heat pump work great for retrofits and new constructions.
In Summary
Ground-source and air-source pumps are powered by electricity. They each have pros and cons, which allows homeowners to choose the right solution to meet their requirements.
Ground-source heat pumps typically save more energy. This is due to their ability to maintain constant temperatures beneath on the ground, in contrast to air-source heat pump’s use of variable temperatures of air outside of the home.
Drawing energy from beneath the surface of the earth also implies that the system won’t be affected by weather conditions or storms since all the equipment that isn’t indoors is underground. There’s nothing located outside of the home that could be damaged or damaged by changes in weather.
Converting temperatures of air can consume greater energy than the conversion of ground temperatures. This is the reason ASHPs require more energy than GSHPs. On the plus side, ASHP systems may cost less upfront, and usually provide a higher return on your investment in moderate climates. However, they will lose their value as temperatures in the outdoors drop.
